Wednesday, August 30, 2017
Monday, August 21, 2017
Friday, August 18, 2017
Thursday, August 17, 2017
Tuesday, August 15, 2017
Monday, August 14, 2017
Tuesday, August 8, 2017
Gradle Vs Maven
Both are used for same purpose but gradle is new and fast in terms of setup and execution also developer
needs to write less code in gradle as compared to maven
needs to write less code in gradle as compared to maven
Showing LapTop Screen on LED
Showing Laptop Dispaly on LED/LCD Screen
1)Right Click with mouse on destop
2)Choose Dispaly settings
3)On Display tab go to multiple displays drop down
and select duplicate these displays and apply
1)Right Click with mouse on destop
2)Choose Dispaly settings
3)On Display tab go to multiple displays drop down
and select duplicate these displays and apply
Monday, August 7, 2017
Preparing for JSF Application Development
Preparing for JSF Application Development
To prepare for JSF application development, you should:
- Make sure that the Java EE: Java Server Faces plugin is enabled. This plugin is bundled with the IDE and enabled by default. However, you may have disabled it for some reason by now.
- Create a project or module with JSF support enabled, or enable JSF support in an existing module.
On this page:
- Making sure that the Java Server Faces plugin is enabled
- Enabling JSF support when creating a project or module
- Enabling JSF support for an existing module
Making sure that the Java Server Faces plugin is enabled
- Open the Settings dialog (e.g. Ctrl+Alt+S).
- In the left-hand part of the dialog, select Plugins.
- In the right-hand part of the dialog, on the Plugins page, type
facesin the search box. As a result, only the plugins whose names and descriptions containfacesare shown in the list of plugins. - If the check box to the right of Java EE: Java Server Faces is not selected, select it.
- Click OK in the Settings dialog.
- If suggested, restart IntelliJ IDEA.
Enabling JSF support when creating a project or module
- Do one of the following:
- If you are going to create a new project: click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project.As a result, the New Project wizard opens.
- If you are going to add a module to an existing project: open the projectyou want to add a module to, and select File | New | Module.As a result, the New Module wizard opens.
- If you are going to create a new project: click Create New Project on the Welcome screen or select File | New | Project.
- On the first page of the wizard, in the left-hand pane, select Java Enterprise. In the right-hand part of the page, specify the JDK to be used and select the Java EE version to be supported.
- If, at this step, you are ready to specify the application server you are going to deploy your application to (e.g. to test the application behavior), do so. This will result in the corresponding server-specific run/debug configurationfor your module generated automatically. Otherwise, to be able to run your application, you will have to create the run/debug configuration yourself.Select the server from the list or click New and select the server of interest. Then, specify the server settings:
- For a server installed locally, specify the path to the server installation directory. (Click
 to select the directory in the corresponding dialog.)
to select the directory in the corresponding dialog.) - For a hosted server (Cloud Foundry or CloudBees), specify your user account details.
- For a server installed locally, specify the path to the server installation directory. (Click
- Under Additional Libraries and Frameworks, select the Web Applicationcheck box.
- Select the JSF check box.If you want the configuration file
faces-config.xmlto be created, select the Create faces-config.xml check box.Select the required library option and, if necessary, specify the associated settings. You can choose to:- Download and use a JSF implementation library (Mojarra).
Now, to view or modify the associated options, click Configure, and in the Downloading Options dialog that opens:
- Select the library version.
- Specify the library name.
- Select the library level (global, project, or module).
- Under Files to download, select which of the files you want to download.
- Under Copy downloaded files to, specify the path to the destination folder. If you want to change the default path, click
 and specify the folder location in the dialog that opens.
and specify the folder location in the dialog that opens.
- Use a JSF library IntelliJ IDEA is already aware of.
- Create a new library using the appropriate JAR files available on your computer.To do that, click Use library and then click Create. Select the required JAR files in the dialog that opens. (For multiple selection, keep the Ctrl key pressed.)If necessary, configure the new library (for example, change its name or level). To do that, click Configure and specify the required settings in the Create Library dialog.
- Postpone setting up the library until a later time. In this case, select Set up library later.
- Download and use a JSF implementation library (Mojarra).
- If you are going to use a JSF component library or libraries (e.g. PrimeFaces, RichFaces, etc.), select the corresponding check box or check boxes and specify the associated options. The procedure is similar to that for the JSF implementation library.
- Specify the name and location settings. For more information, see Project Name and Location or Module Name and Location.
As a result, your new module will contain:
- The
webandWEB-INFdirectories. - The file
index.xhtmlin thewebdirectory. With minor modifications, you can use this file as a starting page of your application. - In the
WEB-INFdirectory, if specified: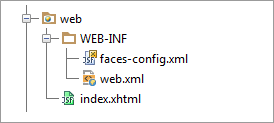
- If specified, the JSF library or libraries included in the module dependencies.
- An artifact specification for you module.
- If you have specified the server, a run/debug configuration for running your application in the context of that server.
Enabling JSF support for an existing module
- Open the Project tool window (e.g. View | Tool Windows | Project).
- Right-click the module and select Add Framework Support.
- In the left-hand pane of the Add Frameworks Support dialog, select the Web Application check box.In the right-hand part of the dialog, select the version of the Servlet specification to be supported from the Versions list.
- Select the JSF check box.If you want the configuration file
faces-config.xmlto be created, select the Create faces-config.xml check box.Select the required library option and, if necessary, specify the associated settings. You can choose to:- Download and use a JSF implementation library (Mojarra).
Now, to view or modify the associated options, click Configure, and in the Downloading Options dialog that opens:
- Select the library version.
- Specify the library name.
- Select the library level (global, project, or module).
- Under Files to download, select which of the files you want to download.
- Under Copy downloaded files to, specify the path to the destination folder. If you want to change the default path, click
 and specify the folder location in the dialog that opens.
and specify the folder location in the dialog that opens.
- Use a JSF library IntelliJ IDEA is already aware of.
- Create a new library using the appropriate JAR files available on your computer.To do that, click Use library and then click Create. Select the required JAR files in the dialog that opens. (For multiple selection, keep the Ctrl key pressed.)If necessary, configure the new library (for example, change its name or level). To do that, click Configure and specify the required settings in the Create Library dialog.
- Postpone setting up the library until a later time. In this case, select Set up library later.
- Download and use a JSF implementation library (Mojarra).
- If you are going to use a JSF component library or libraries (e.g. PrimeFaces, RichFaces, etc.), select the corresponding check box or check boxes and specify the associated options. The procedure is similar to that for the JSF implementation library.
- Click OK in the Add Frameworks Support dialog.
Wednesday, August 2, 2017
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
